What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to create items from thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics. It involves injecting heated material into a mold cavity, which cools and solidifies into the desired shape. This process allows for the mass production of complex parts with high accuracy and repeatability, making it one of the most popular plastic fabrication methods. Let’s explore injection molding in more detail.
How Does Injection Molding Work?
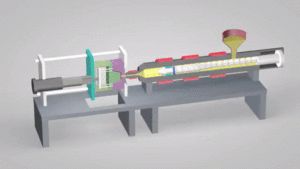
Injection molding involves melting plastic pellets and injecting them into custom-designed molds using an injection machine. The machine forces plastic through a nozzle at high pressure, filling the mold cavity evenly with molten material. A cooling system then circulates cold water or air around the hole to help the material solidify quickly. After the item has hardened completely, it is removed from the cavity, and any excess material is trimmed away.
The Advantages of Injection Molding
Injection molding offers numerous advantages over other manufacturing processes, including:
• Cost-effectiveness – As one of the most cost-effective manufacturing processes, injection molding can produce large volumes of high-quality parts with minimal waste. It also requires less labor than other fabrication methods, reducing business costs.
• Efficiency – With injection molding machines capable of producing hundreds or even thousands of identical parts per hour, production times are greatly reduced compared to traditional machining processes. This helps ensure that orders can be filled quickly and deadlines can be met easily in fast-paced industries like automotive or medical device manufacturing.
• Precision – With precision components designed to extremely tight tolerances made possible by 3D CAD modeling software, injection molded parts offer superior accuracy and repeatability compared to other plastic fabrication methods such as CNC machining or manual assembly.
Injection Mold Tool Material Types
Most molds used in injection molding operations are aluminum or hard steel (generally made from H13 tool steel). Aluminum molds are typically used when low quantities are required, while hard steel tools are favored when high-volume production runs must be achieved quickly and economically. However, aluminum molds have shorter lifespans than steel tools due to their softer nature, so they cannot handle as much wear and tear over time as their harder counterparts before needing replacement or repair work.
In summary, injection molding is a powerful tool for creating intricate parts quickly and accurately at scale compared to traditional manufacturing processes like CNC machining or manual assembly. It requires special tools designed from aluminum or hard steel, which will determine how long each device will last before needing maintenance or replacement, depending on how much wear and tear it experiences during operation. Ultimately, companies should choose between these two materials based on their specific needs; aluminum may be better suited for short-run projects, while hard steel may be more suitable for high-volume runs requiring greater longevity from each tool set up in the injection machine. Knowing what type of tool material you need for your project’s requirements is just one part of successful injection molded part design. At Concept 274, we can help you decide which type of mold is better suited for your production plans.


